Ready to revolutionize your data journey with Infoveave?
Recent Blogs
- How Data Automation And Data Engineering Are Transforming Healthcare
- How Data Automation Tools Are Transforming Manufacturing
- How Data Automation and Data Engineering Are Revolutionizing the Telecom Industry
- How Data Automation is Powering the Retail Energy Industry
- How Data Automation and Data Engineering Are Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry
Data Governance Using a Unified Data Platform
What is data governance?
At its core, data governance is the formal, business-wide strategy for managing data as a critical asset. It defines who is responsible for the data (data ownership), what policies and procedures apply to it, and how it can be used to achieve business goals. Think of it as the rulebook for your data. It's not just about technology; it's about the people, processes, and technology working together to ensure data is trustworthy and accessible.
For a business leader, the benefits of data governance are tangible and directly impact the company's success.
-
Risk Mitigation: Data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA have made data management a legal and financial risk. A solid data governance framework ensures you have the controls in place to maintain compliance, protect sensitive information, and avoid costly fines and reputational damage.
-
Competitive Advantage: When you can trust your data, you can make smarter, faster decisions. Whether it's identifying a new market opportunity, optimizing supply chains, or understanding customer behavior, high-quality data provides the insights needed to outperform the competition.
-
Customer Trust: Customers are more aware than ever of how their personal data is handled. By demonstrating a commitment to data privacy and security through robust governance, you build trust and loyalty, which are invaluable assets in today's market.
Key Components of Data Governance
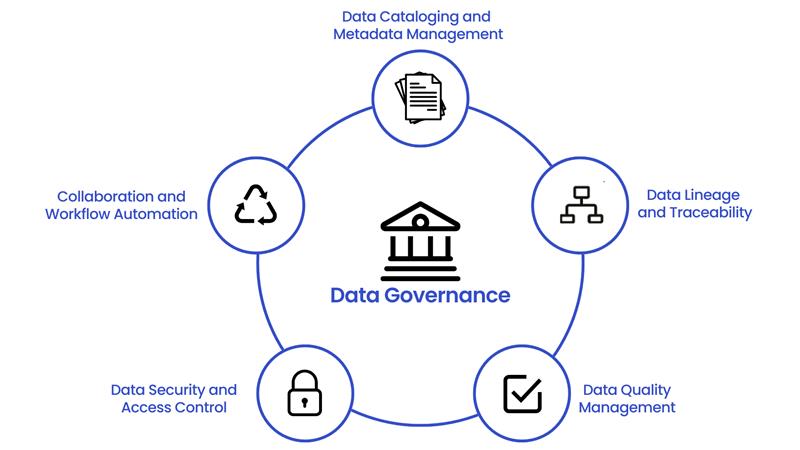
Data governance is built on several foundational pillars. Understanding them is key to appreciating its scope.
-
Data Quality: This is the cornerstone. It ensures that your data is fit for its intended purpose. Key dimensions include:
-
Accuracy: Is the data correct? (e.g., Is the customer's name spelled correctly?)
-
Completeness: Are all the necessary data fields filled? (e.g., Is the shipping address missing the zip code?)
-
Consistency: Is the data uniform across different systems? (e.g., Is the same customer listed as "John Smith" in one system and "J. Smith" in another?)
-
Timeliness: Is the data up-to-date and available when needed?
-
-
Data Security: This involves protecting data from unauthorized access and threats, both internal and external. It's about building a fortress around your data using measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and robust access controls.
-
Data Privacy: While related to security, privacy is distinct. Security protects data from unauthorized access, while privacy dictates how data is used by authorized individuals. It involves honoring customer preferences and complying with regulations about the collection, use, and sharing of personally identifiable information (PII).
-
Data Accessibility: This is about ensuring the right people can get the right data at the right time to do their jobs, without compromising security or privacy. It involves creating a "data democracy" where employees are empowered with information, often through tools like data catalogs that make it easy to find and understand available data.
-
Data Catalog: This is the centralized inventory of datasets, metadata, and business definitions, giving every authorized user a single, trusted reference for locating data. It captures details like ownership, refresh frequency, and quality scores, enabling teams to assess reliability and reduce duplication of effort.
-
Data Lineage: This maps the entire lifecycle of data from source to transformation to destination. It highlights downstream impacts of changes, allowing teams to trace errors quickly and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Data Classification: This categorizes data by sensitivity and business value (e.g., public, internal, confidential), ensuring appropriate security and retention policies. Uses automated tagging to enforce encryption and access controls, reducing manual oversight and strengthening regulatory compliance.
-
Data Discovery and Sharing: This enables employees to easily search for and evaluate datasets across departments, fostering collaboration and informed decision-making. Provides secure, permission-based sharing with audit trails so data can be exchanged responsibly while maintaining compliance.
Infoveave's Business Impact: Simplifying Governance for easy adoption
For many organizations, the primary obstacle to implementing data governance is complexity. Governance must be simplified for easier understanding and adoption. Infoveave integrates all essential governance capabilities into a single, user-friendly platform, making it easy to manage your data assets with confidence and clarity.
-
Find and Define Your Data Instantly: Infoveave's Data Catalog and Business Glossary work together to create a searchable, easy-to-understand map of your entire data landscape. Teams can quickly locate the right data and are aligned on what it means, accelerating analysis and eliminating ambiguity.
-
Get Access to Trusted Data effortlessly: AI-powered Data Quality checks validate and reconcile data on a scheduled basis, so users always work with accurate, up-to-date information.
-
Assign Clear Ownership and Structure: Organize your data into Domains and Projects that reflect your business units. This creates instant clarity on who is responsible for what data, fostering a culture of accountability from the ground up.
-
Tag, Classify, and Secure with Ease: Use Tagging to classify data by sensitivity and importance. Then, apply powerful Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information, simplifying compliance and mitigating risk.
-
Integrate Governance into Every Workflow Infoveave makes governance an inherent part of your data operations—automating compliance and ensuring every data-driven decision is built on trusted, well-managed information.
-
Audit your data : This ensures that every change made to data can be traced and reviewed. It provides complete visibility into who accessed or modified data, when it was done, and why. This transparency helps organizations demonstrate compliance, investigate issues, and maintain accountability across all data processes.
By integrating these critical governance functions into one user-friendly platform, Infoveave transforms data governance from a theoretical challenge into a practical, achievable business advantage.
Driving Confident Decisions with Strong Governance
Data governance isn’t just about compliance; it’s about creating a foundation of trust that drives smarter decisions, faster operations, and stronger business outcomes. By bringing governance, quality, and access together in one Unified Data Platform, Infoveave makes it easier for teams to work confidently with reliable data every day. With governance seamlessly integrated into your data workflows, you can focus on what matters most—turning data into measurable business impact.
Ready to simplify data governance and gain complete control over your enterprise data? Book a demo with Infoveave today.