Data Governance Primer: A Strategic Guide
Every modern business runs on data, whether it is a retail brand tracking customer purchases, a logistics firm monitoring shipments, or a financial institution managing millions of transactions every day. Yet, even as organizations collect more data than ever before, many still face a persistent question: can they truly trust their data?
Can leaders rely on the numbers in their reports to make strategic decisions? Can business users find the right data without depending on IT? Can decision makers act confidently, knowing their insights are based on accurate, consistent, and compliant data?
These questions define the purpose of data governance.
Data governance is not a new concept, but its importance grows as organizations adopt multiple systems, expand globally, and face increasing regulatory and operational pressures. A strong governance foundation ensures that data remains visible, reliable, and secure across the enterprise.
This primer helps business leaders understand how to build a working data governance framework using Infoveave’s Data Management Platform, a unified solution designed to bring structure, accountability, and clarity to complex data environments. The primer highlights a challenge typically encountered in the Retail space and provides a detailed solution on how it can be addressed by implementing a robust Data Governance framework using Infoveave’s data management platform
Lessons from Retail and Beyond
Consider the case of a growing retail enterprise As the brand expands its presence across physical stores, online marketplaces, and mobile applications, it begins to integrate new sales channels, logistics networks, and cloud-based systems. Every department considers itself “data driven.” Operations uses logistics data to optimize deliveries, finance monitors sales and reconciles revenue, and procurement tracks supplier data for better negotiations.
But despite this abundance of information, decision making becomes slow and fragmented.
During a quarterly review, the Chief Operating Officer presents a report showing a 98 percent on-time shipment rate, a critical operational KPI. Moments later, the Chief Financial Officer shares a conflicting figure: a 15 percent rise in refund requests for delayed deliveries. Both teams are right, but their definitions differ. Operations marks a shipment as “on time” once it leaves the warehouse, while Finance counts it only when the customer confirms delivery.
This simple difference exposes a deeper issue: each team defines, manages, and measures data in its own way.
The misalignment causes more problems than just confusion. Product data inconsistencies between the e-commerce platform and warehouse system lead to costly errors. A customer ordering a blue variant receives a red one instead. Annual financial audits turn into stressful marathons as teams scramble to trace figures and prove accuracy. What was once a manageable inconvenience now threatens efficiency, trust, and profitability.
The company realizes the issue is not the lack of data, but the lack of trust in data.
At this inflection point, the leadership team chooses to implement a structured approach using Infoveave’s Data Management Platform, treating data not as a byproduct of operations but as a strategic enterprise asset.
Assembling the Team
One of the most common misconceptions about data governance is that it belongs solely to IT. In practice, effective governance is a collaborative business discipline. Infoveave supports this collaboration by defining clear roles, responsibilities, and workflows that connect strategy with execution.
Leadership and effective governance
The company appoints a Chief Data Officer (CDO) to lead the initiative. Reporting directly to executive leadership, the CDO acts as a bridge between business goals and data management. Their mandate is to ensure that every data initiative aligns with business outcomes, improving efficiency, reducing risk, and enhancing customer experience.
With Infoveave, the CDO gains access to a centralized governance workspace where data strategy, stewardship workflows, and access policies operate cohesively.
A Data Governance Council is formed to provide oversight. Comprising senior leaders from key functions such as Finance, Operations, Supply Chain, and Legal, the council acts as the decision making authority.
Defining Roles: Ownership and Stewardship
Each major business domain such as Customer, Product, Finance, Supply Chain, and HR is assigned a Data Owner.
A Data Owner, typically a senior business leader, is responsible for the quality, security, and ethical use of data in their domain. For example, the VP of Supply Chain becomes the Data Owner for vendor, logistics, and inventory data.
Infoveave enables Data Owners to monitor their domain’s data health through visual quality metrics and lineage insights.
Supporting them are Data Stewards, subject matter experts embedded within business teams. A Steward in the Finance department, for instance, manages day-to-day data validation, investigates anomalies, and reviews access requests. Using Infoveave Stewards can collaborate directly with business users, track issue resolution, and document data quality actions without manual intervention.
These structured roles transform governance from policy to practice. Every stakeholder, from executives to analysts, becomes an active participant in maintaining data integrity and trust.
Building Your Data Governance Framework
Implementing data governance is not about introducing new bureaucracy. It is about introducing order, visibility, and accountability.
With Infoveave’s Data Management Platform, businesses build their governance framework in a structured, iterative way that aligns governance activity with tangible business outcomes.
Step 1: Cataloging Data Assets in Infoveave
Visibility is the foundation of governance. You cannot govern what you cannot see. Most organizations spend an extraordinary amount of time locating data. Analysts send endless emails, rely on institutional memory, and waste hours searching on shared drives. This inefficiency introduces risk and inconsistency, often leading to the use of outdated or unverified datasets.
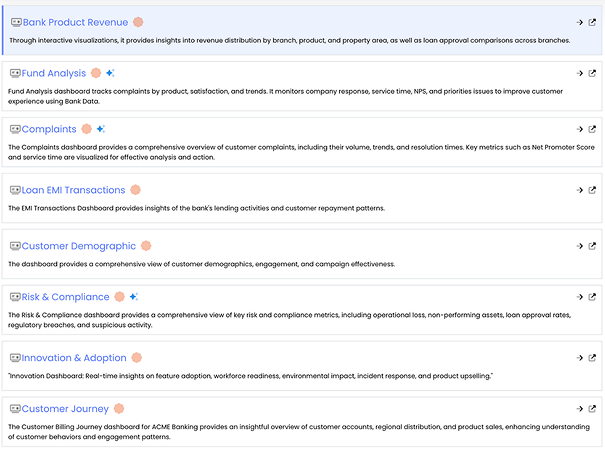
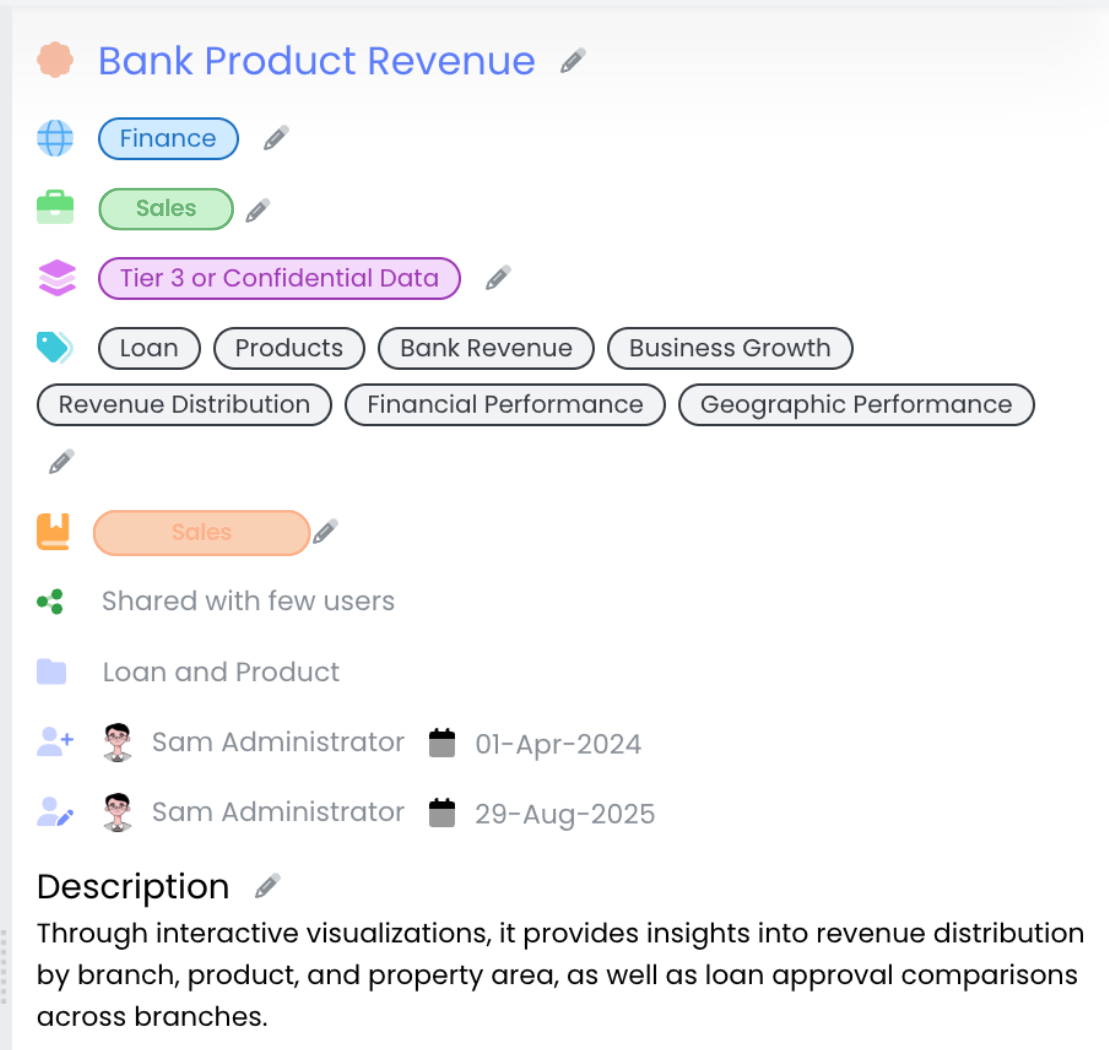
As soon as the organization connects its databases , and cloud applications, Infoveave automatically scans and indexes every dataset. It extracts technical metadata such as schemas, data types, and refresh frequency, and enriches it with business context like definitions, ownership, and data quality status using GenAI.
Within minutes, every stakeholder, from business users to data analysts, can discover, understand, and trust the data they work with.
For example, when a finance analyst searches for “Revenue by Channel,” Infoveave’s catalog surfaces certified datasets linked to this attribute, ensuring that every team uses the same definitions and trusted inputs.
Outcome:
The organization gains a unified view of its data landscape. Silos disappear. Analysts spend time analyzing rather than searching. Decision makers trust the numbers in front of them.
Step 2: Organizing Data into Business Domains
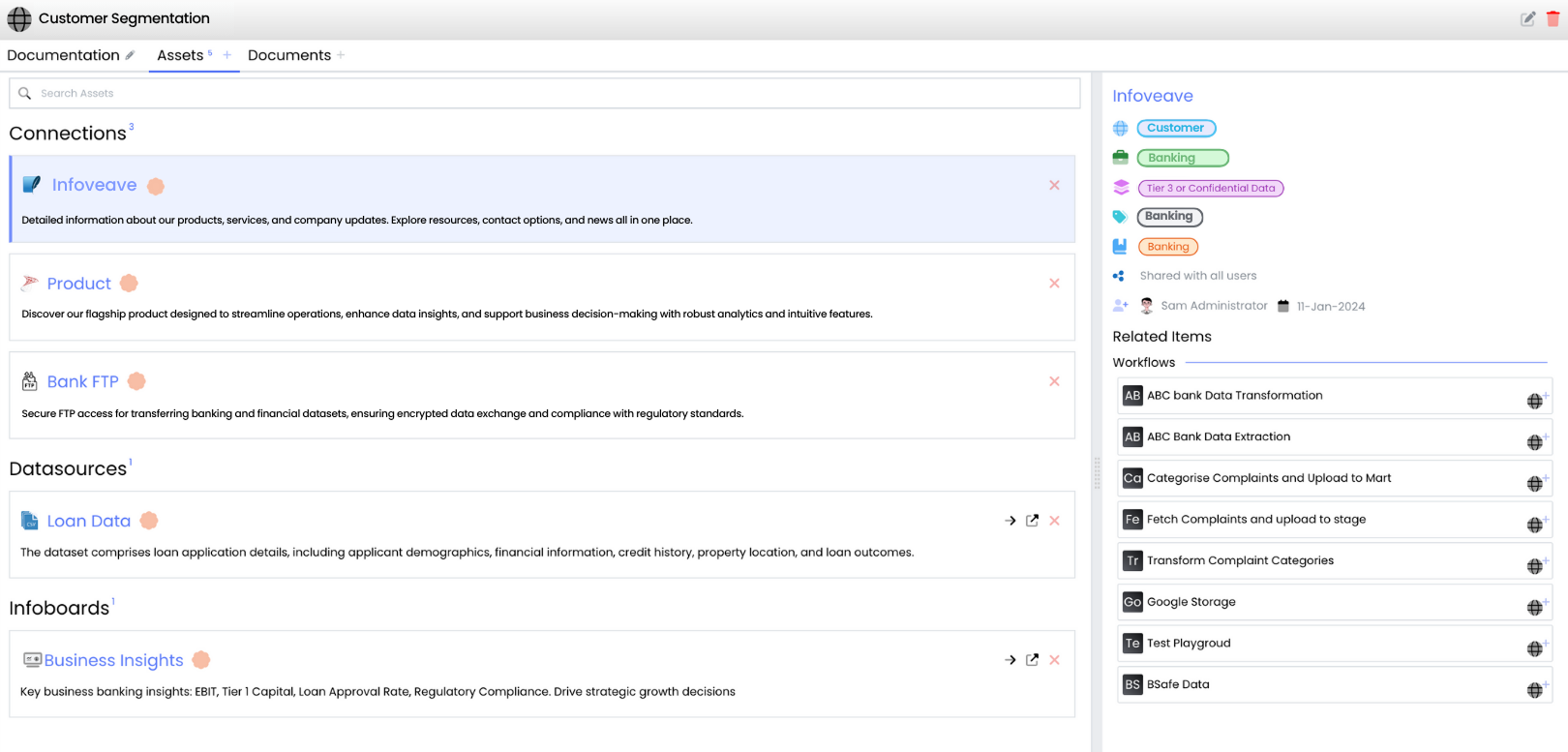
Once visibility is established, Infoveave helps businesses organize data into Business Domains that reflect operational structure. This step creates order out of chaos and embeds accountability into data management.
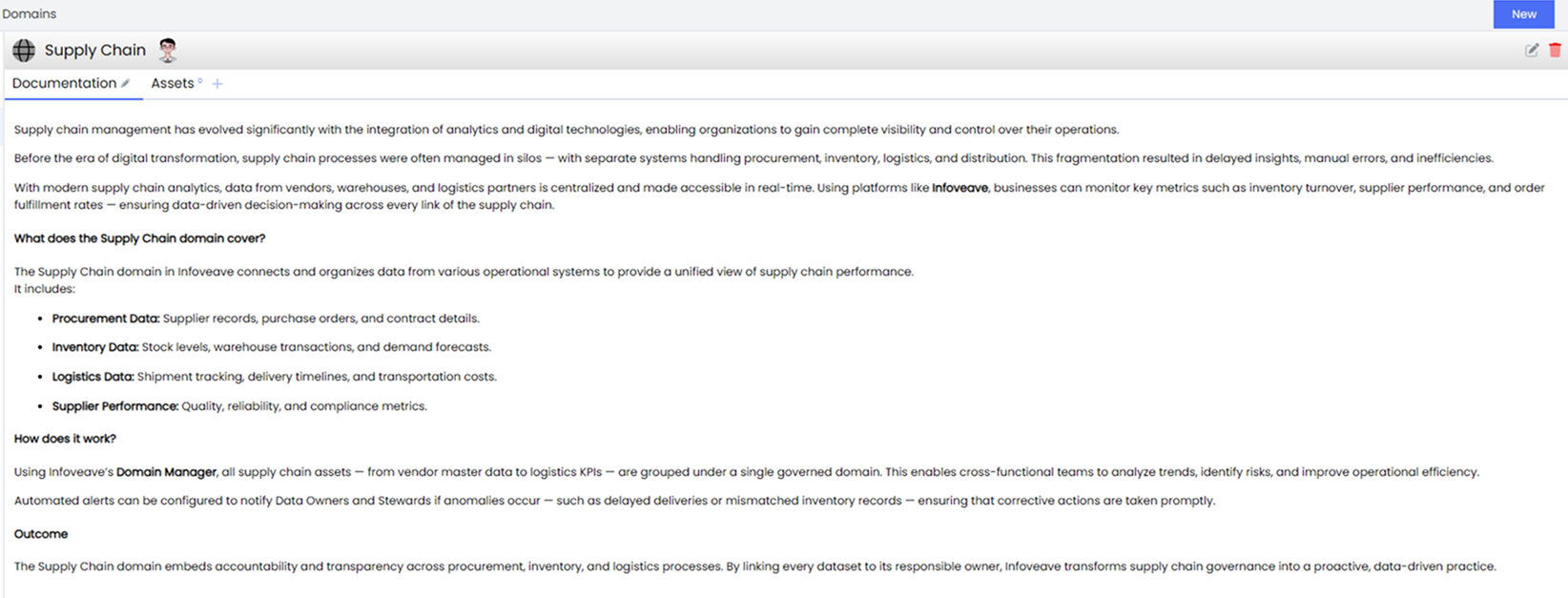
Using Infoveave’s Domain Manager, the governance team groups all assets under structured domains such as:
-
Customer: Data about acquisition, loyalty, and engagement.
-
Product: Specifications, pricing, and lifecycle details.
-
Supply Chain: Vendor, inventory, and logistics records.
-
Finance and Risk: Transactions, compliance, and audit trails.
-
Human Resources: Employee lifecycle and workforce data.
Each domain is then mapped to a Data Owner in Infoveave. The assignment is visible across the organization, ensuring that every dataset has an accountable owner and responsible steward.
If an issue arises, such as inconsistent inventory counts, the governance platform automatically routes alerts to the VP of Supply Chain and their assigned Stewards, who can investigate directly from their dashboards.
This closed-loop accountability system replaces manual escalation chains with automated, transparent workflows.
Outcome:
Data accountability becomes embedded into the organization’s structure. Every dataset is owned, managed, and continuously monitored, turning governance from a theoretical framework into daily operational discipline.
Step 3: Aligning Governance with Projects
A governance program succeeds only when it delivers measurable value. Infoveave ensures that governance activities are directly tied to ongoing business projects, making governance a visible enabler of business results, not an administrative overhead.
For example, consider a retail company struggling with inventory imbalances, frequent stockouts of high-demand products, and overstock of low-moving items. The supply chain team launches an initiative called Real Time Inventory Optimization.
Infoveave plays a central role in operationalizing this initiative:
The Data Steward defines quality rules within Infoveave, ensuring stock-level data updates every 15 minutes and product identifiers remain consistent across systems.
The data owner monitors data completeness and accuracy against predefined thresholds.
The Governance Council tracks progress and compliance directly through Infoveave’s reporting layer, linking data improvements to cost reductions and improved fulfillment accuracy.
As data quality stabilizes, the company observes measurable improvements: fewer shipment errors, better supplier coordination, and optimized warehouse utilization. The connection between data quality and business value becomes distinctive.
Infoveave’s strength lies in embedding governance directly into operations. By tying governance metrics to business KPIs, it transforms data management into a driver of performance improvement.
Outcome:
Governance evolves from a static framework to an operational practice. Business teams recognize governance not as a control mechanism but as a capability that enables faster, smarter, and more reliable decision making.
Step 4: Creating a Common Language with the Business Glossary
As organizations expand, terminology tends to diverge. “Customer,” “order,” or “on-time shipment” may mean different things to different departments, leading to miscommunication, conflicting KPIs, and misaligned reporting.

Infoveave addresses this through its integrated Business Glossary, a centralized repository of business terms and definitions linked directly to the data catalog.
Using Infoveave, Data Stewards and Owners collaborate to define terms that align with enterprise-wide understanding. Each term in the glossary contains:
-
Standardized Definition
-
Associated Data Assets
-
Linked Domain and Steward
These definitions automatically synchronize with data assets, dashboards, and reports, ensuring consistency across the organization.
Outcome:
Teams across business units start speaking the same language. Reports align, KPIs become comparable, and trust in data deepens. The glossary becomes a living bridge between business understanding and data execution.
Step 5: Prioritizing Protection — Classifying Data by Tier
Infoveave’s Data Classification Framework lets enterprises prioritize protection through five governance tiers:
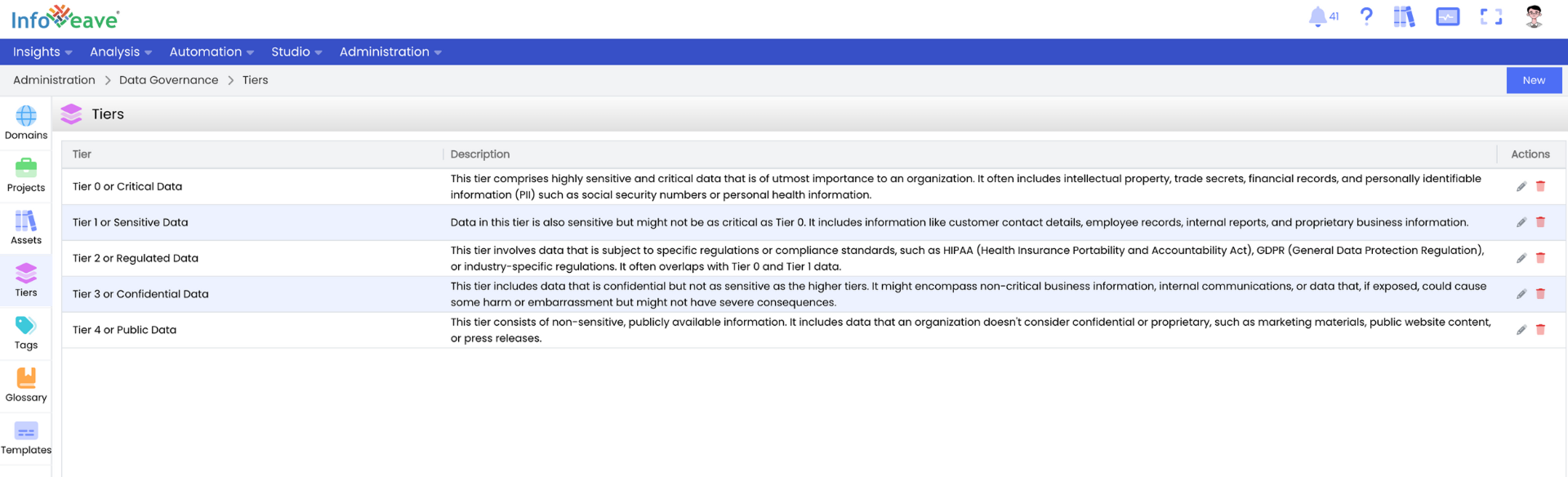
Tier 0 – Critical Data
Highly sensitive, mission-critical data such as intellectual property, trade secrets, financial statements, and PII. Infoveave enforces the strictest monitoring, encryption, and approval policies for these assets.
Tier 1 – Sensitive Data
Important but slightly less critical information, including customer contact details, employee records, and internal business reports. Infoveave applies controlled access and continuous quality validation.
Tier 2 – Regulated Data
Data governed by standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Infoveave automatically enforces regulation-specific controls, from consent management to data residency.
Tier 3 – Confidential Data
Operational information such as vendor communications or internal analytics that require privacy but lower restriction. Infoveave maintains audit visibility while allowing day-to-day accessibility.
Tier 4 – Public Data
Open or published materials such as marketing assets or press releases. Infoveave tracks usage for accuracy but imposes minimal control.
Outcome:
Governance resources focus on data where impact and risk are highest, ensuring both efficiency and security.
Step 6: Managing Access with Precision
Infoveave’s Role Based Access Control (RBAC) model aligns permissions with user roles and tier classifications.
Examples:
-
Finance Analysts: read-only access to Tier 0 and Tier 1 financial datasets.
-
Customer Support Agents: view order and shipment data (Tier 2) with PII masked.
-
External Partners: receive anonymized feeds (Tier 3 or Tier 4) with no sensitive exposure.
Outcome:
Employees gain secure, friction-free access while leadership retains full oversight of who accesses what, when, and why.
Step 7: Mapping Data Lineage
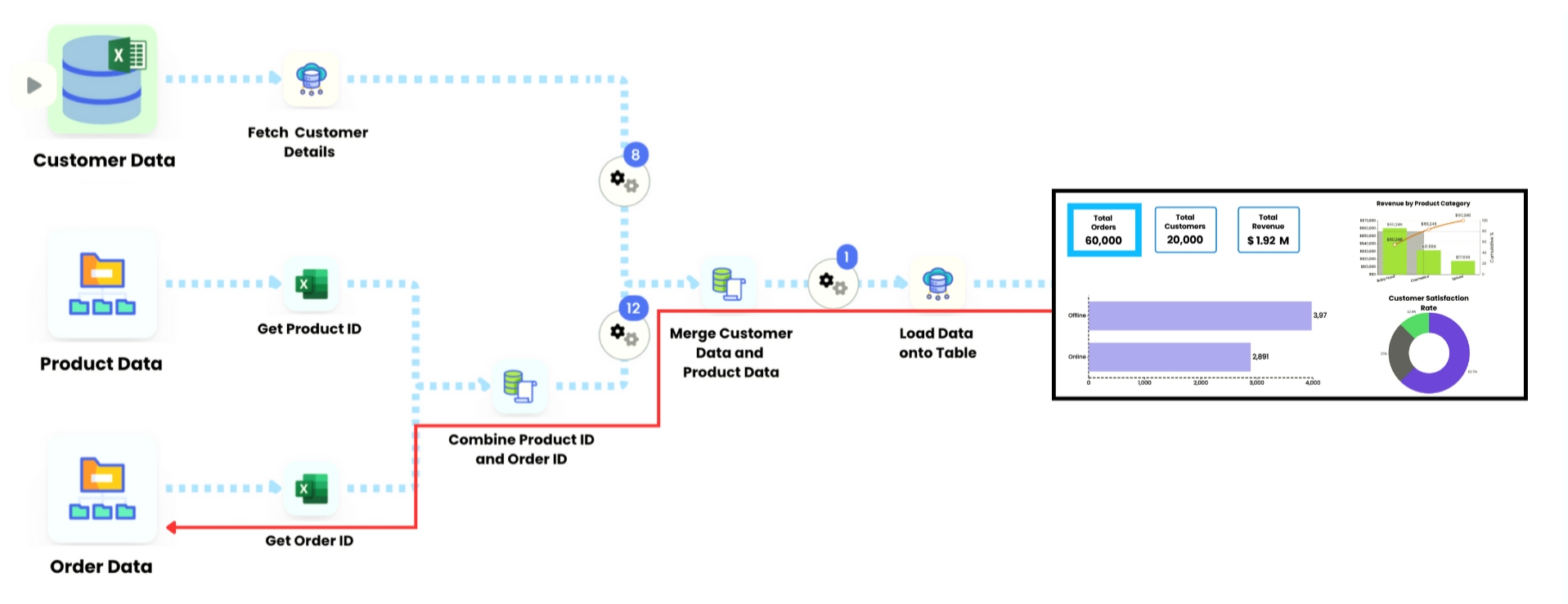
Infoveave’s Data Lineage visualizes the entire lifecycle of data, from origin through transformation to final consumption.
If a revenue figure on a dashboard is questioned, lineage traces it instantly back to source transactions, revealing every filter and calculation along the way.
Outcome:
Complete transparency builds confidence in analytics, accelerates audits, and makes root-cause analysis nearly instantaneous.
Step 8: Embedding Security and Compliance by Design
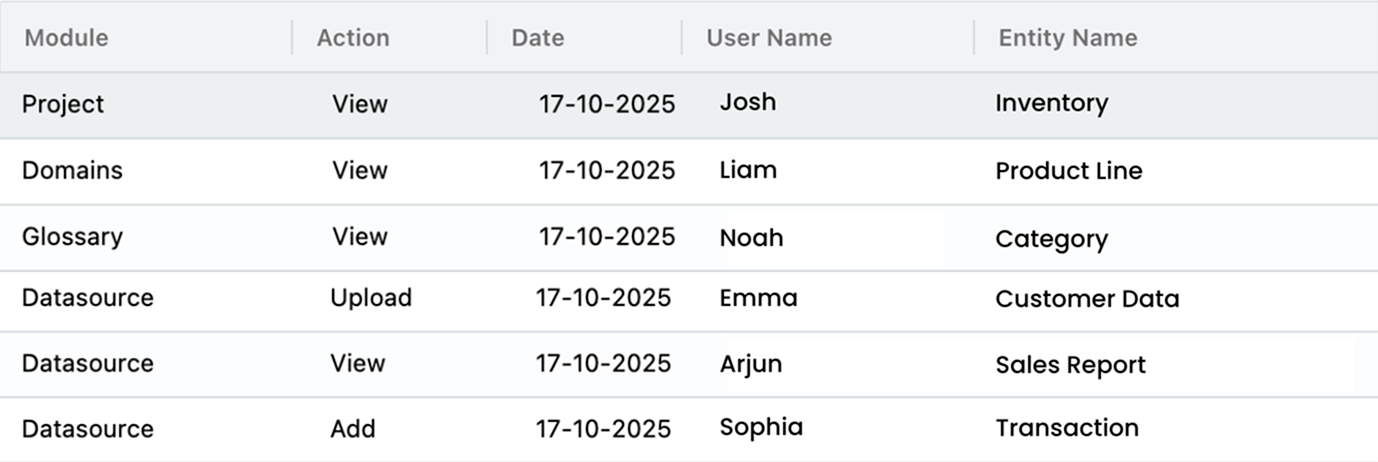
Infoveave operationalizes compliance rather than treating it as documentation.
Automated Policies: Rules tied to data tiers, for instance, GDPR-tagged datasets automatically apply residency and deletion requirements.
Immutable Audit Trails: Every action, view, edit, or export, is logged.
Outcome:
Audits become predictable check-ins instead of disruptions, and compliance shifts from reactive reporting to proactive assurance.
Step 9: Building a Culture of Data Responsibility
Governance thrives when it becomes habit. Infoveave sustains this through automated alerts, issue tracking, and continuous feedback loops.
If a supplier record fails validation, a workflow instantly notifies the assigned Data Steward, who investigates, corrects, and documents the resolution within the platform.
Across the enterprise:
-
Supply chain teams rely on accurate, real-time metrics.
-
Finance closes books faster with verified figures.
-
Leaders make decisions with confidence.
Outcome:
Data quality turns into a shared responsibility supported by automation and visibility.
Governance becomes part of everyday business rhythm.
Closing Note: Turning Governance into Growth
Data governance is not about restriction, it is about confidence. Infoveave’s Data Management Platform unifies discovery, quality, compliance, and access so organizations can trust their data and scale securely.
By embedding governance in Infoveave, businesses gain:
-
A single view of all data assets.
-
Automated accountability through workflows.
-
Continuous monitoring for quality and compliance.
-
Secure, role-based access without slowing innovation.
Infoveave provides everything needed to operationalize governance, from data cataloging and lineage to access control, compliance automation, and stewardship workflows.
Discover how Infoveave helps your enterprise manage data with clarity, accountability, and confidence.
Explore Infoveave’s Data Management Platform. Book a demo today.